Introduction
The internet, a revolutionary invention, has transformed how we live, work, and communicate. Understanding its history gives us a glimpse into the rapid technological advancements that have shaped our world. From its humble beginnings as a military project to its current status as a global communication network, the internet’s evolution is a testament to human ingenuity and collaboration.
The Origins of the Internet

Early Concepts and Theoretical Foundations
The idea of a global network predated the Internet for several decades. Visionaries like J.C.R. Licklider of MIT, who envisioned an “Intergalactic Computer Network,” laid the groundwork for future developments. His ideas inspired many early pioneers in computer science.
The Role of ARPANET
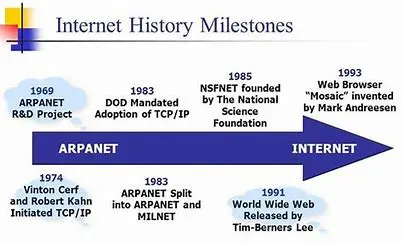
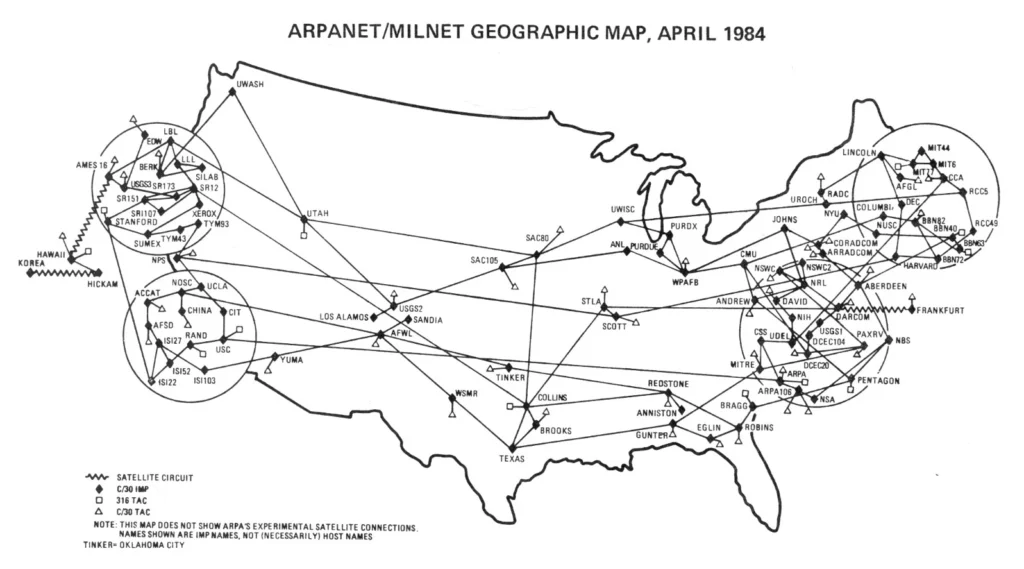
The ARPANET, funded by the U.S. Department of Defense’s Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), is often considered the precursor to the Internet. Launched in 1969, ARPANET connected universities and research institutions, allowing for sharing of information and resources.
Key Milestones in the Development of the Internet
The Introduction of Packet Switching
Packet switching, a method of data transmission where data is broken into packets before being sent, was crucial to the development of the Internet. This technology, developed by Paul Baran and Donald Davies independently, allowed for more efficient and reliable communication.
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
In the 1970s, Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn developed the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which became the standard for data transmission over the Internet. This protocol suite enabled different networks to connect and communicate with each other.
The Birth of Email
Email, one of the first applications of the ARPANET, was developed in the early 1970s by Ray Tomlinson. This innovation allowed users to send messages to each other, revolutionizing communication.
The Transition from ARPANET to the Internet
The Establishment of the Domain Name System (DNS)
Introduced in 1983, the Domain Name System (DNS) made it easier to navigate the internet by mapping domain names to IP addresses. This system, developed by Paul Mockapetris, remains a fundamental part of Internet infrastructure.
The Growth of the Internet in the 1980s
During the 1980s, the Internet expanded beyond the confines of academic and research institutions. The National Science Foundation Network (NSFNET) played a significant role in this expansion by connecting more networks and increasing bandwidth.
The World Wide Web Revolution
Tim Berners-Lee and the Creation of the Web
In 1989, Tim Berners-Lee, a scientist at CERN, proposed the World Wide Web, a system for sharing information via hypertext. By 1991, the first website was launched, marking the beginning of the web as we know it.
The Emergence of Web Browsers
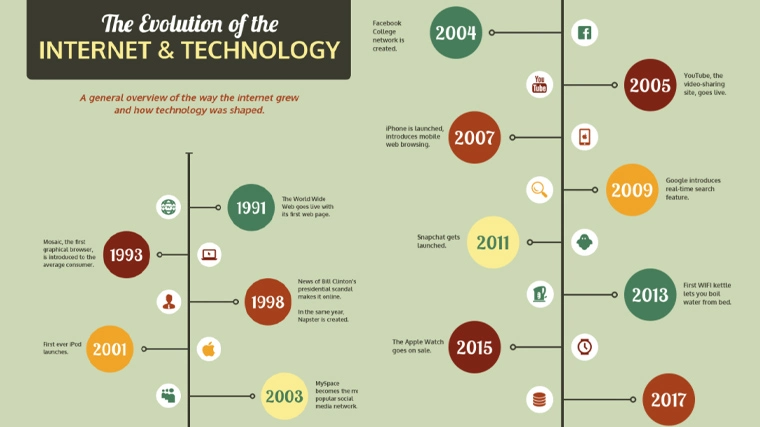
The development of web browsers, such as Mosaic in 1993 and Netscape Navigator in 1994, made the web more accessible to the general public. These browsers introduced graphical interfaces, which enhanced user experience.
The Dot-Com Boom and Bust
The late 1990s saw a surge in internet-based businesses, leading to the dot-com boom. However, the bubble burst in 2000, resulting in significant financial losses and paving the way for more sustainable growth.
The Social Media and Web 2.0 Era

The Rise of Social Media Platforms
The early 2000s saw the rise of social media platforms like Friendster, MySpace, and eventually Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. These platforms revolutionized how people interact, share information, and build communities online.
The Evolution of User-Generated Content
Web 2.0, characterized by user-generated content, collaboration, and interactivity, transformed the internet. Platforms like YouTube, Wikipedia, and blogs empowered users to create and share content, democratizing information.
Mobile Internet and the Smartphone Revolution
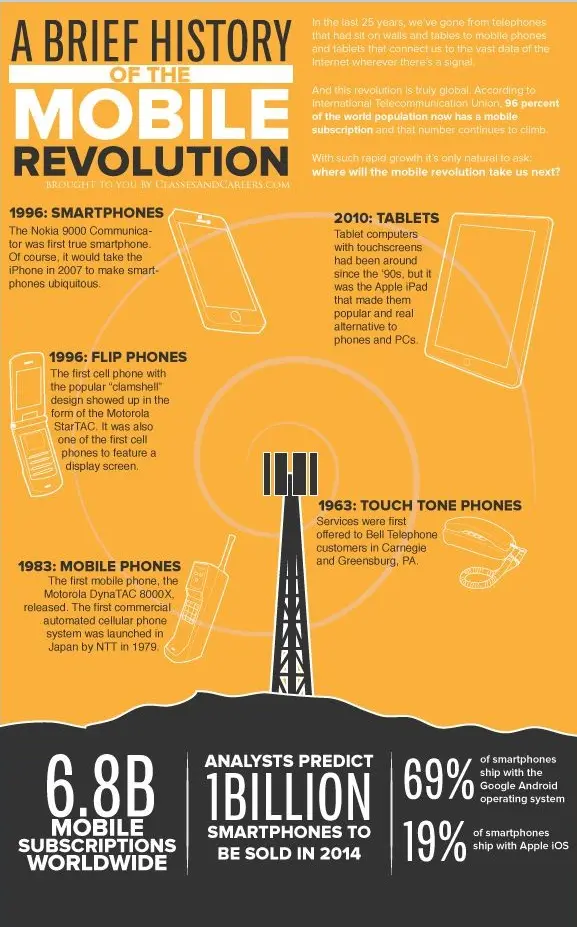
The Impact of Smartphones
The introduction of smartphones, particularly the iPhone in 2007, revolutionized how people access the internet. Mobile internet usage surpassed desktop usage, leading to the development of mobile-friendly websites and applications.
The Role of Apps and Services
Apps and services like WhatsApp, Uber, and Spotify changed how people communicate, travel, and consume media. The app ecosystem continues to grow, offering a wide range of functionalities and services.
Want to dive deeper into digital trends? Check out our post on Digital Marketing tips for more insights.
The Internet of Things (IoT)
Connecting Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data. From smart home devices to wearable technology, IoT transforms everyday life by making it more convenient and efficient.
Security and Privacy Concerns
With the proliferation of connected devices, concerns about security and privacy have become more pronounced. Ensuring the safety and integrity of data in an increasingly interconnected world is a significant challenge.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Enhancing User Experience
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) enhance user experiences online. From personalized recommendations to advanced search algorithms, AI is making the internet more intuitive and responsive.
Ethical Considerations
The use of AI and ML raises ethical questions, particularly regarding data privacy, bias, and the potential for misuse. Addressing these concerns is crucial as these technologies continue to evolve.
The Future of the Internet

Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like 5G, quantum computing, and blockchain are poised to shape the future of the internet. These technologies promise faster, more secure, and more decentralized internet experiences.
Challenges and Opportunities
The future of the internet presents both challenges and opportunities. Ensuring equitable access, addressing cybersecurity threats, and maintaining a free and open internet are critical issues that must be addressed.
The Deep Web vs. Dark Web: Unraveling the Mystery
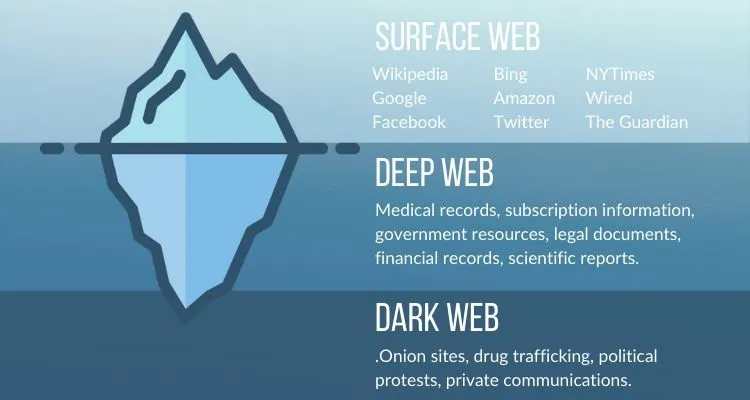
The Deep Web: The Invisible Backbone
The Deep Web refers to all the parts of the internet that aren’t indexed by traditional search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo. This vast, invisible portion of the internet includes everything from your private emails, online banking records, and social media messages to academic databases, subscription-only content, and government resources. Unlike the surface web, which can be easily accessed through simple search queries, the Deep Web is hidden from public view because its content is either password-protected, encrypted, or stored in databases that aren’t linked to standard search engines.
Despite its somewhat mysterious name, the Deep Web plays a crucial role in the functioning of the Internet. It provides the secure infrastructure needed for private communication, sensitive data storage, and countless legitimate activities that require privacy and confidentiality. Whether it’s your personal information stored in cloud services, medical records, or confidential business data, the Deep Web ensures these remain out of reach from unauthorized access. Far from being a shadowy corner of the internet, the Deep Web is integral to maintaining the security and integrity of the online world.
The Dark Web: The Underworld of the Internet
The Dark Web is a smaller, deliberately concealed segment of the Deep Web that can only be accessed using specialized software like Tor (The Onion Router). Unlike the broader Deep Web, the Dark Web is notorious for being associated with illegal activities, including drug trafficking, illegal arms sales, and various forms of cybercrime. However, it’s important to recognize that not everything on the Dark Web is illicit; it also serves as a refuge for whistleblowers, journalists, activists, and others who seek anonymity, especially in oppressive regimes where freedom of speech is restricted.
Accessing the Dark Web requires tools that anonymize user data, making it extremely difficult to track online activity. This level of anonymity is both the Dark Web’s greatest strength and its most significant flaw, as it attracts those who wish to hide their activities, whether for legitimate reasons or criminal purposes. Despite its notorious reputation, the Dark Web brings to light critical discussions about privacy, security, and the balance between freedom and regulation in the digital age. As society continues to grapple with these issues, the Dark Web remains a complex and multifaceted part of the internet landscape.
Environmental Impact of the Internet

Energy Consumption and Data Centers
The internet’s infrastructure, including data centres, consumes significant energy. As internet usage grows, so does its environmental footprint, raising concerns about sustainability.
Sustainable Practices and Innovations
Efforts to reduce the environmental impact of the Internet include energy-efficient data centres, renewable energy sources, and sustainable technology practices. These innovations aim to minimize the internet’s carbon footprint.
Are you interested in learning more about the dark web? Explore this to complete the guide and understand its complexities and risks.
Cybersecurity Threats and Solutions
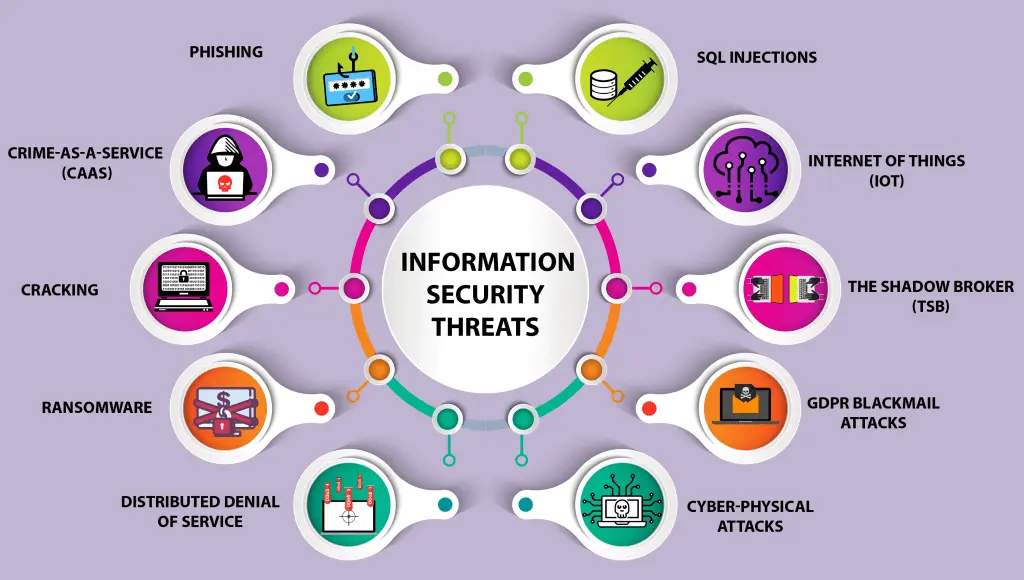
Overview of Common Cybersecurity Threats
The digital landscape is fraught with various cybersecurity threats, each posing unique challenges to users and organizations alike. Malware, a broad term for malicious software, can disrupt or damage systems by infiltrating networks through deceptive means like infected emails or compromised websites. Phishing attacks exploit human psychology, using deceptive emails or websites that appear legitimate to trick users into revealing sensitive information such as passwords and financial details. These attacks often target large groups but can be customized for specific individuals in a tactic known as spear phishing. Ransomware is another formidable threat, encrypting a victim’s data and demanding payment for its release, often leaving organizations crippled until the ransom is paid or data is restored from backups.
Strategies for Cybersecurity
To combat these threats, various cybersecurity strategies are employed. Encryption is one of the foundational security measures, protecting data by transforming it into a coded format that is unreadable without a proper decryption key. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains inaccessible to unauthorized users. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access to a system or account. This could include something the user knows (a password), something they have (a smartphone or security token), and something they are (biometric verification like a fingerprint). By combining these strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their defences against the growing sophistication of cyber threats.
Conclusion
Reflecting on the Journey
The history of the internet is a testament to human ingenuity and collaboration. From its humble beginnings to its current global presence, the internet has transformed how we live, work, and connect.
The Future Outlook
As we look to the future, the internet will continue to evolve, bringing new challenges and opportunities. Embracing innovation and addressing critical issues will shape the next chapter of the internet’s story.
FAQs
What was the first message sent over the ARPANET?
The first message sent over the ARPANET was “LO,” which was an attempt to log in to a remote system. The system crashed before the entire word “LOGIN” could be transmitted.
Who is considered the father of the Internet?
Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn are often referred to as the fathers of the internet due to their development of the TCP/IP protocols.
When was the World Wide Web introduced to the public?
Tim Berners-Lee introduced The World Wide Web to the public in 1991.
What caused the dot-com bubble to burst?
The dot-com bubble burst in 2000 due to the overvaluation of internet companies, which led to a market crash and significant financial losses.
How has social media changed the internet?
Social media has transformed the internet by enabling real-time communication, user-generated content, and the formation of online communities.
What are the main security concerns with the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The main security concerns with IoT include data breaches, unauthorized access, and the potential for hacking, which can compromise the integrity and privacy of connected devices.

One Comment